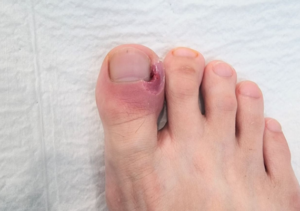
Paronychia is a common nail condition characterized by an infection of the skin surrounding a fingernail or toenail. It can be acute or chronic, depending on the duration and cause of the infection. Acute paronychia typically develops rapidly, while chronic paronychia persists for longer periods and can recur frequently.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!
Causes of Paronychia
- Bacterial Infection: Acute paronychia is often caused by bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus species, usually following an injury to the nail area.
- Fungal Infection: Chronic paronychia is commonly caused by Candida species and other fungi.
- Injury or Trauma: Cuts, hangnails, or excessive nail biting can introduce bacteria or fungi, leading to infection.
- Moisture Exposure: Prolonged exposure to water or moist environments can weaken the skin around the nails, making it more susceptible to infection.
- Chemical Irritants: Frequent exposure to harsh chemicals, detergents, or solvents can damage the skin around the nails, leading to paronychia.
- Underlying Skin Conditions: Conditions such as eczema or psoriasis can increase the risk of developing paronychia.