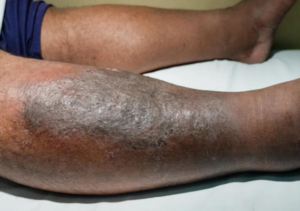
Cellulitis is a bacterial skin infection that can affect deeper layers of the skin, often caused by streptococcus or staphylococcus bacteria entering through a break in the skin. It’s important to recognize the symptoms and seek prompt treatment to prevent complications.
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!
Causes of Cellulitis
- Bacterial Entry: Bacteria enter the skin through cuts, scrapes, insect bites, or surgical wounds.
- Skin Conditions: Conditions like eczema or athlete’s foot can create openings for bacteria.
- Weak Immune System: Reduced immunity increases susceptibility to infections.
- Lymphatic System Issues: Impaired lymphatic drainage can contribute to bacterial buildup.